| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
| 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 |
| 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 |
| 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 |
| 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
- boolean배열
- 행열. 2중반복문..
- 그럼 int배열의 deefault값은?????
- 생활코딩
- while문이 틀린이유?? math.random()을 사용해서푸는법?
- form.getImageFies 오타났음
- ㅓㅂ
- (참고로 boolean 배열의 default 값은 false 이다.
- 마지막에 배열의 foreach구문이 틀린것같은데 ...... 저게왜틀린건지나는잘모르겠슴다.
- 출처:구멍가게코딩단-코배스(개정판)
- bindingresult 쓰니까 에러났다. 어떻게해야하냐;;
- Today
- Total
푸린세스
DOM(3) - HTML Element 본문
HTMLElement
getElement* 메소드를 통해서 원하는 객체를 조회했다면 이 객체들을 대상으로 구체적인 작업을 처리해야 한다. 이를 위해서는 획득한 객체가 무엇인지 알아야 한다. 그래야 적절한 메소드나 프로퍼티를 사용할 수 있다.
아래 코드는 getElement*의 리턴 값을 보여준다.
실행결과
이것을 통해서 알 수 있는 것은 아래와 같다.
- document.getElementById : 리턴 데이터 타입은 HTMLLIELement
- document.getElementsByTagName : 리턴 데이터 타입은 HTMLCollection
즉 실행결과가 하나인 경우 HTMLLIELement, 복수인 경우 HTMLCollection을 리턴하고 있다.
interface HTMLLIElement : HTMLElement {
attribute DOMString type;
attribute long value;
};interface HTMLAnchorElement : HTMLElement {
attribute DOMString accessKey;
attribute DOMString charset;
attribute DOMString coords;
attribute DOMString href;
attribute DOMString hreflang;
attribute DOMString name;
attribute DOMString rel;
attribute DOMString rev;
attribute DOMString shape;
attribute long tabIndex;
attribute DOMString target;
attribute DOMString type;
void blur();
void focus();
};즉 엘리먼트 객체에 따라서 프로퍼티가 다르다는 것을 알 수 있다. 하지만 모든 엘리먼트들은 HTMLElement를 상속 받고 있다.
(자식객체) (부모객체)
interface HTMLLIElement : HTMLElement {
interface HTMLAnchorElement : HTMLElement {
HTMLElement는 아래와 같다.
interface HTMLElement : Element {
attribute DOMString id;
attribute DOMString title;
attribute DOMString lang;
attribute DOMString dir;
attribute DOMString className;
};링크는 DOM의 스팩이다.
Document Object Model HTML
1.6.1. Property Attributes HTML attributes are exposed as properties on the element object. The DOM naming conventions always determine the name of the exposed property, and are independent of the case of the attribute in the source document. The data type
www.w3.org
DOM Tree
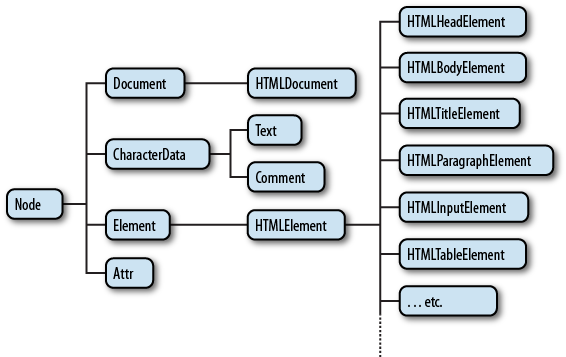
모든 엘리먼트는 HTMLElement의 자식이다. 따라서 HTMLElement의 프로퍼티를 똑같이 가지고 있다. 동시에 엘리먼트의 성격에 따라서 자신만의 프로퍼티를 가지고 있는데 이것은 엘리먼트의 성격에 따라서 달라진다. HTMLElement는 Element의 자식이고 Element는 Node의 자식이다. Node는 Object의 자식이다. 이러한 관계를 DOM Tree라고 한다.
이러한 관계를 이해하지 못하면 필요한 API를 찾아내는 것이 어렵거나 몹시 혼란스러울 것이다. 다행인 것은 jQuery와 같은 라이브러리를 이용한다면 이러한 관계를 몰라도 된다. 혹시 이해가 안된다고 너무 상심하지 말자
